|
Ø
产品中心
北京: 电话:010-84369508 |
Ø
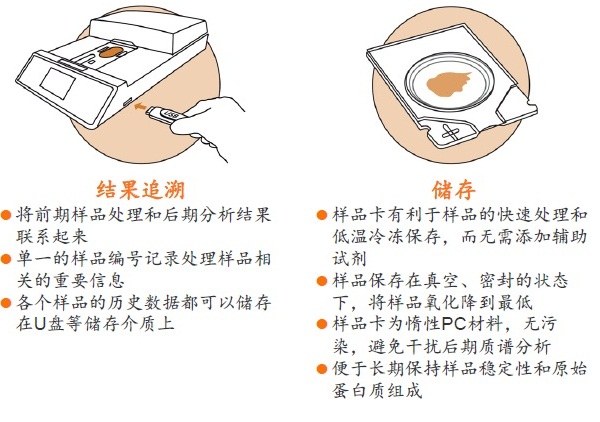
Stabilizor T1 生物样品稳定仪
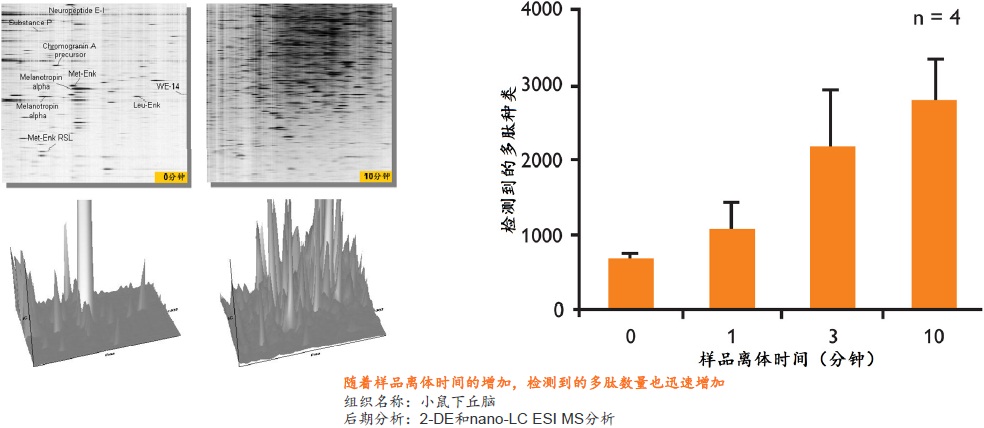
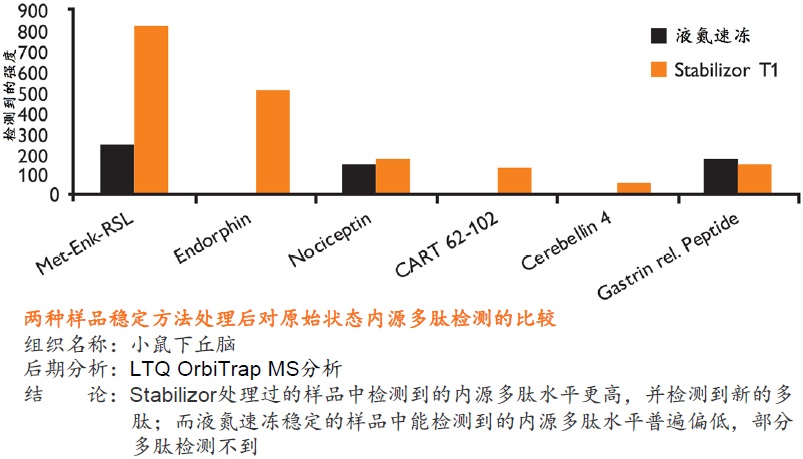
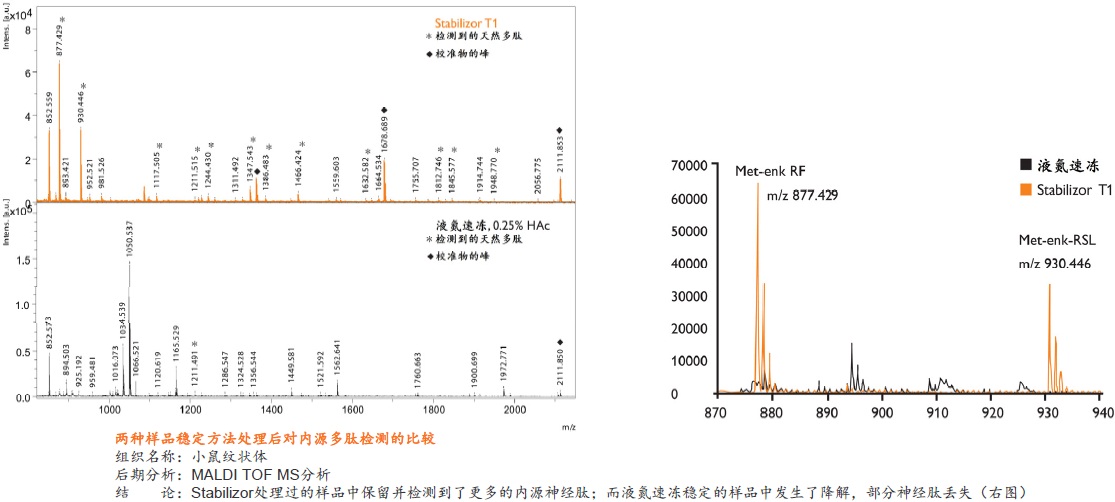
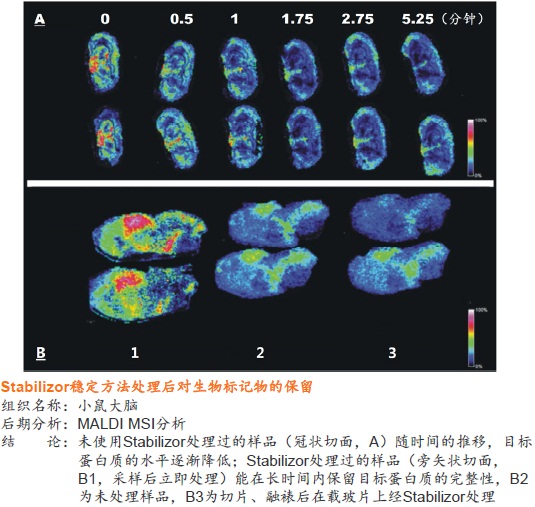
在蛋白质组研究中,要得到准确可靠的结果,很大程度上取决于样品的前处理方法。保持样品的稳定性,即样品是否反映目标蛋白质在活体内的原始状态则尤为重要。一旦样品从机体分离,调控平衡被打破,对于某些蛋白质或多肽,离体降解是一个很快速的过程。降解导致蛋白质的种类、含量和修饰快速变化,使得检测到的部分蛋白质或肽段实际上是高丰度蛋白质的降解产生的片段,而不是样品的原始蛋白质(如下图)。
在细胞和组织表达的蛋白质组中,发挥重要生理功能、最具研究意义和价值的蛋白质通常是一些含量很小、稳定性差的低丰度蛋白质或多肽。随着蛋白质检测技术的发展,检测方法的灵敏度越来越高,也对样品前处理方法提出了更高的要求,如何在处理样品过程中保留这些蛋白质或多肽就变得越来越重要。
因此采用一种快速、有效的样品稳定方法,尽量缩短样品采集与稳定之间的间隔时间并将样品前处理过程标准化,对于蛋白质研究具有重要意义。高质量的样品前处理有利于获得高质量的数据,进而增强分析结果的可靠性和可比性。
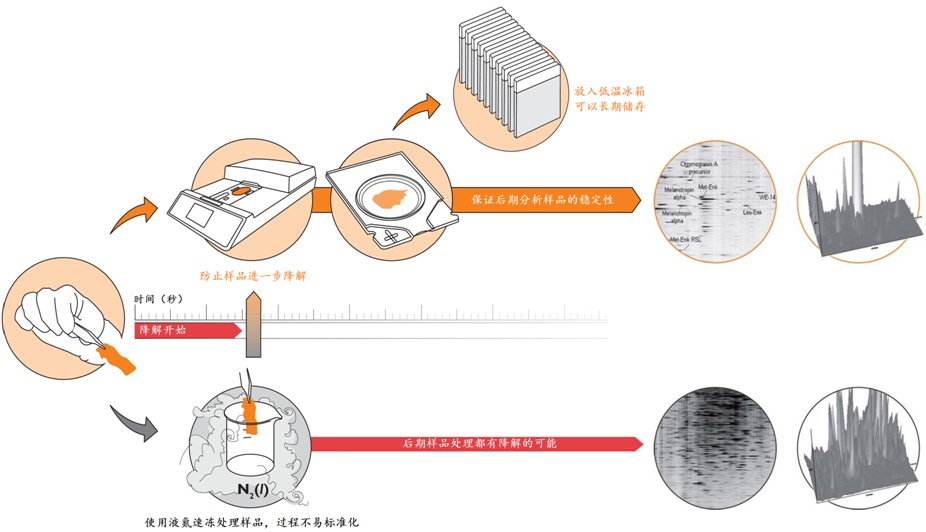
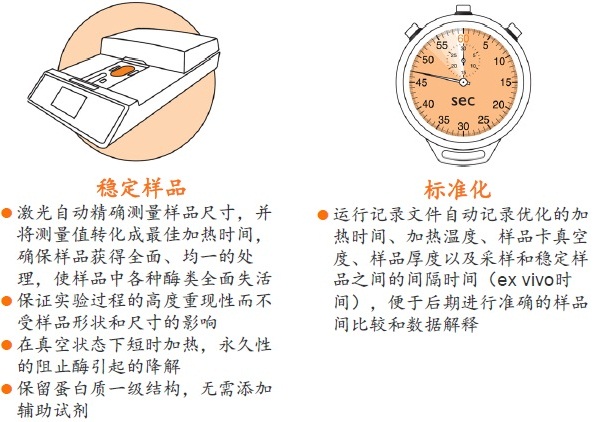
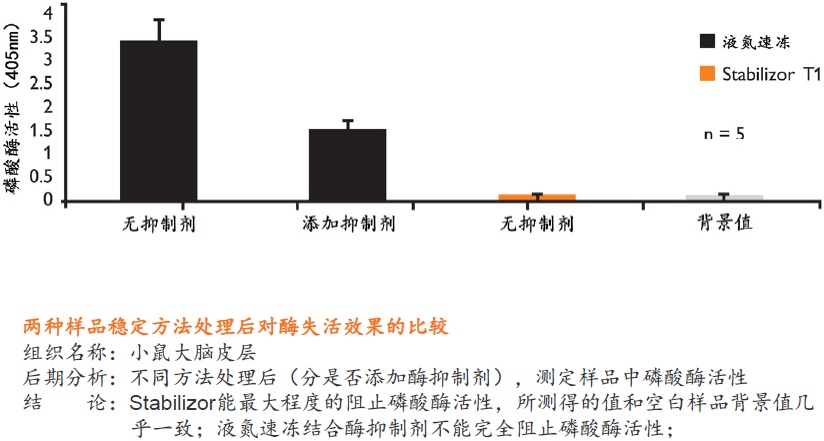
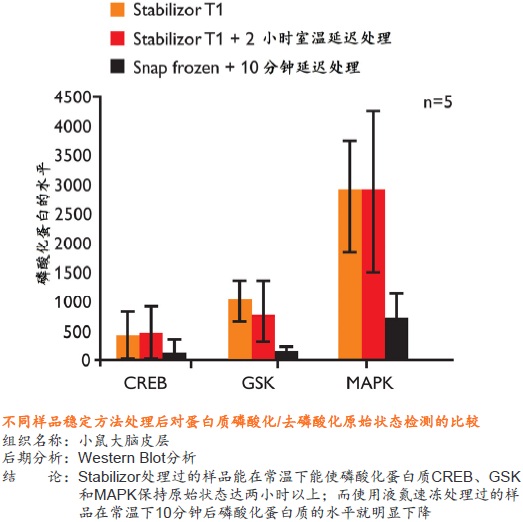
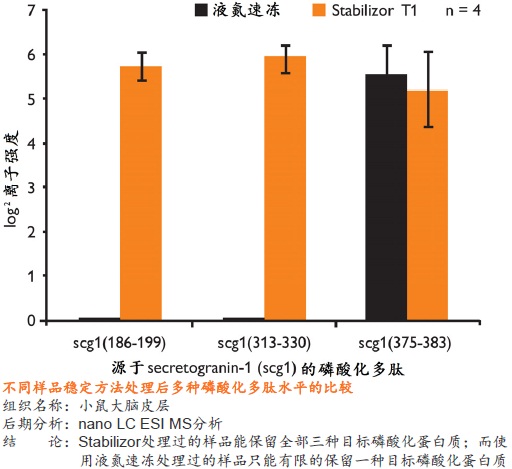
Stabilizor系统是瑞典Denator公司的专利生物样品稳定技术。该系统包含Stabilizor T1主机和Maintainor样品卡,用于解决蛋白质离体降解的难题。Stabilizor系统能快速、均匀、准确的将热量传递给样品,破坏蛋白质中的氢键,保留氨基酸链的共价肽键,即破坏蛋白质的二级及以上结构,保留一级结构的完整性。这种不可逆的失活效应将样品中的各种酶类失活,从而将蛋白质离体降解的程度降到最低。处理过程中无需添加辅助抑制试剂,也将后期分析的干扰因素降到了最低。
使用Stabilizor系统无需添加辅助抑制试剂即可永久性的去除蛋白酶和磷酸酶的活性,防止蛋白质降解发生。降低蛋白质组的复杂性,减少高丰度蛋白质降解片段的干扰,增加分析和发现具有重要价值的蛋白质/多肽生物标记物的可能性。Stabilizor处理样品具有的稳定性、标准化和可追溯性,更易得到高质量的分析数据。
液氮速冻结合酶抑制剂是目前广泛使用的阻止样品降解的标准方法。但这种方法会破坏细胞膜和细胞结构,使得样品融化后,降解和修饰蛋白质的酶分布得更广泛,导致更多蛋白质或其修饰形式发生改变。而且这种方法具有可逆性和选择性,无法全面的阻止样品中酶类的活性,添加的试剂还会干扰后期样品分析,部分试剂具有一定毒性。
使用Stabilizor系统的优势:
● 是一种纯物理的样品稳定方法,不需使用干扰后期分析的酶抑制剂 ● 处理时间短,一般在一分钟以内即可将样品中的各种酶类失活 ● 有利于保留样品在活体内蛋白质的磷酸化和其它翻译后修饰的真实状态,保留不稳定、易降解的低丰度蛋白质 ● 避免了样品中低丰度蛋白质或多肽受高丰度蛋白质降解片段的干扰,有助于发现新的蛋白质、多肽以及它们的修饰形式
● 永久性的去除蛋白酶和磷酸酶的活性,样品经稳定后,即可在常温下进行制备操作,无需担心酶对蛋白质、多肽的降解或改变它们的修饰形式 ● 降低蛋白质组的复杂程度,缩小动态范围,增加分析和发现具有重要价值的蛋白质或多肽生物标记物的可能性
● 使用方便,在采样的同时即可稳定样品,缩短样品离体降解的时间
● 样品采集和储存的过程高度标准化,使分析结果更加可靠,数据更具可比性,便于进行比较蛋白质组研究
● 使用MALDI-MSI检测目标蛋白质或多肽,Stabilizor是目前最为有效的样品稳定方法
技术参数:
Stabilizor T1主机
● 4.3英寸彩色触摸显示屏 ● 对样品卡施加真空压力范围:10—100mbar ● 噪音:低于45分贝 ● 样品尺寸测量激光分级:CLASS 1蓝色激光 ● 内置处理器:1 GHz×86,内存为1GB ● 操作系统:Linux开源软件 ● 三个USB接口 ● 外部尺寸(L×W×H):465×306×143mm ● 净重: 6.7kg ● 功率:最高为350瓦,正常使用为70瓦,待机为20瓦 ● 电源:100-240V/50-60Hz ● 使用环境温度:10—40℃ ● 使用环境最大相对湿度:80%(无凝结) Maintainor样品卡
● 外部尺寸(L×W×H):85×54×2mm ● 样品腔尺寸:高7mm,直径33mm ● 使用环境最大相对湿度:85%(无凝结) ● 材质:PC,带特氟龙涂层 ● 适用温度:-80—100 ℃
Stabilizor系统有助于揭示真正的蛋白质组、多肽组和磷酸化图谱
订货信息:
使用Stabilizor处理样品所发表的部分文章Loss of correlations among proteins in brains of the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome. Ahmed et al., J. of Proteome research. 2012. Just accepted Read more Sample Preparation Techniques for the Untargeted LC-MS-Based Discovery of Peptides in Complex Biological Matrices. Finoulst et al., J. Biomedicine and Biotechnology. 2011. Read more Extensive Characterization of Tupaia belangeri Neuropeptidome Using an Integrated Mass Spectrometric Approach. Petruzziello et al., J. Proteome Res. 2011, ahead of print. Read more Effect of Thaw Temperatures in Reducing Enzyme Activity in Human Thyroid Tissues. Kokkat et al., Biopreservation and Biobanking. 2011, ahead of print. Read more Thermal stabilization of tissues and the preservation of protein phosphorylation states for two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Smejkal et al., Electrophoresis 2011, Volume 32, pages 2206–2215. Read more Biomarkers of disease and post-mortem changes-heat stabilization, a necessary tool for measurement of protein regulation. Kultima et al., Journal of Proteomics, 2011 In press. Read more Benefits of heat-treatment to the protease packed neutrophil for proteome analysis: Halting protein degradation. Kennedy et al., Proteomics 2011, 11, pages 2560–2564 Read more Neuropeptide profiling of the bovine hypothalamus: Thermal stabilization is an effective tool in inhibiting post-mortem degradation. Colgrave et al., Proteomics 2011, 11, 1264-1276 Read more Methodology and technology for stabilization of specific states of signal transduction proteins. Borén M., Methods Mol Biol. 2011;717:91-100 Read more Preserving protein profiles in tissue samples: Differing outcomes with and without heat stabilization, M Ahmed et al, Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 2011 Mar 15;196(1):99-106 Read more Clinical application for the preservation of phospho-proteins through in-situ tissue stabilization, CB Rountree et al, Proteome Science, 2010; 8: 61 Read more Stopping the clock on proteomic degradation by heat-treatment at the point of tissue excision. Richard J. A. Goodwin et al. Proteomics, Volume 10, Issue 9, pages 1751-1761, No. 9 May 2010 Read more Mass Spectrometric Imaging for Biomedical Tissue, Chughtai, K. and. Heeren, R.M.A, Analysis, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110 (5), pp 3237-3277. Read more Neuropeptidomic analysis of the embryonic Japanese quail diencephalon, Scholz, B., H. Alm, et al., BMC Dev Biol 10: 30. Read more The use of neuroproteomics in drug abuse research, M Lull et al, Drug and Alcohol Dependence, Volume 107, Issue 1, 1 February 2010, Pages 11-22 Read more Impact of temperature dependent sampling procedures in proteomics and peptidomics - A characterization of the liver and pancreas post mortem degradome, B Scholz et al. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, M900229-MCP200, January 28, 2010 Read more Banking of clinical samples for proteomic biomarker studies: A consideration of logistical issues with a focus on pre-analytical variation, Jackson, D.H., and Banks, R.E., Proteomics - Clinical Applications 2010 4:3, 250-270 Read more A report on the ESF workshop on quality control in proteomics, L Martens. Mol. BioSyst., 2010, 6, 935-938 Read more Assessing the use of thermal treatment to preserve the intact proteomes of post-mortem heart and brain tissue, AA. Robinson et al. Proteomics., Article 2009 Oct;9(19):4433-44 Read more Preserving the yeast proteome from sample degradation, J. Grassl et al. Proteomics., Proteomics. 2009 Oct;9(20):4616-26. Read more Development and evaluation of normalization methods for label-free relative quantification of endogenous peptides. K. Kultima, Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, October 1, 2009, 8, 2285-2295. Read more A Quantitative Peptidomic Analysis of Peptides Related to the Endogenous Opioid and Tachykinin Systems in Nucleus Accumbens of Rats Following Naloxone-Precipitated Morphine Withdrawal U. Rossbach et al. J. Proteome Res., Proteomics. 2009 Oct;9(20):4616-26 Read more Heat Stabilization of the Tissue Proteome: A New Technology for Improved Proteomics, M. Svensson et al. J. Proteome Res., 2009, 8 (2), pp 974-981 Read more Sample preparation issues for tissue imaging by imaging MS, Kaletas, B. K., I. M. van der Wiel, et al. Proteomics 9(10): 2622-33 Read more Protein and peptides in pictures: imaging with MALDI mass spectrometry, RJ. Goodwin et al. Proteomics., 2008 Sep;8(18):3785-800 Read more The significance of biochemical and molecular sample integrity in brain proteomics and peptidomics: stathmin 2-20 and peptides as sample quality indicators. K. Sköld et al. Proteomics. 2007 Dec;7(24):4445-56 Read more Neuropeptidomics: MS Applied to the Discovery of Novel Peptides from the Brain M. Svensson et al. Anal. Chem., 2007, 79 (1), pp 14-21 Read more Neuropeptidomics: expanding proteomics downwards. M. Svensson et al. Biochem Soc Trans 2007, 35, (Pt 3), pp 588-93. Read more |
|